Inside Google's Search Algorithm: Insights from the 2024 Leak

Hendrik

Debugging:
- Featured Image URL: https://seo-experiments.net/assets/google-leak-image.webp
- Alt-Text:
1. Introduction
In March 2024, a significant leak of internal Google documents on GitHub provided unprecedented insight into the intricacies of Google's search algorithm. These documents, reportedly from Google's Content API Warehouse, were disseminated by an automated bot named yoshi-code-bot. The documents, later shared with Rand Fishkin, co-founder of SparkToro, and Michael King, CEO of iPullRank, offer a rare glimpse into the factors influencing Google's search rankings.
The 2024 leak of Google's internal documents has opened a new window into the world of search engine optimization (SEO). This article delves deep into these revelations, providing a comprehensive understanding of the various components that shape Google's ranking algorithms.
2. Overview of the Leaked Documents
The leaked documents outline essential elements used by Google to assess and rank content. They highlight 2,596 modules with 14,014 attributes, demotions for inappropriate content, and the enduring significance of link diversity and relevance.
Significance of the Leak
The leak is monumental for several reasons. It confirms long-held suspicions about Google's use of user data and the complexity of its ranking algorithms. It also provides SEO professionals with a roadmap to optimize content more effectively by understanding the underlying mechanics of Google's search rankings.
3. Key Insights from the Leak
Twiddlers and Their Roles
Twiddlers are functions that adjust a document's information retrieval score or its position before being displayed to users. They play a crucial role in fine-tuning search results, promoting diversity, and meeting specific user needs.
NavBoost: Influences search result rankings based on click data.
QualityBoost: Evaluates the quality of results and makes adjustments.
RealTimeBoost: Adapts to real-time events and trends for relevant results.
Importance of Links and PageRank
Links remain a pivotal factor in Google's ranking system. The diversity and relevance of links, along with the PageRank of a website's homepage, continue to be critical for SEO. The documents confirm that Google still heavily relies on the foundational principles of PageRank, albeit in a more nuanced and complex manner.
Evaluation of Click Metrics
Google employs various metrics to gauge click success, such as badClicks, goodClicks, lastLongestClicks, and unsquashedClicks. These metrics help in determining the quality and relevance of content. Understanding how these metrics are calculated and what they signify can help webmasters and SEOs optimize their content to align better with Google's evaluation criteria.
4. Unusual Findings
The documents reveal some surprising elements, such as the use of "hostAge" to sandbox new websites, contradicting Google's public statements. Additionally, the ChromeInTotal module shows that Google uses data from its Chrome browser for ranking purposes, despite previous denials.
Sandbox and HostAge
The "hostAge" attribute, which is used to sandbox new websites, highlights Google's cautious approach to new content. By isolating new sites, Google can prevent potential manipulation and ensure that only reliable and high-quality content rises to the top over time.
Chrome Data Utilization
The use of Chrome data for ranking evaluation is significant. It indicates that Google leverages vast amounts of user interaction data to refine its search results, ensuring that they are as relevant and useful as possible. This data includes user engagement metrics, browsing habits, and other behavioral signals collected through the Chrome browser.
System Architecture
The architecture of Google's ranking system comprises several microservices, including Trawler (Crawling), Alexandria (Indexing), Mustang (Ranking), and SuperRoot (Query Processing). Each of these services plays a specific role in processing and evaluating web content, highlighting the complexity and sophistication of Google's search infrastructure.
5. Detailed Analysis of Ranking Modules
Twiddlers' Impact
Twiddlers modify a document's ranking score or placement just before it's displayed to the user. This process promotes result diversity and caters to specific user needs.
NavBoost
NavBoost, introduced in 2005, collects clickstream data to enhance search quality. Initially, this data was gathered via the Google Toolbar PageRank. The development of the Chrome browser in 2008 was driven by the desire for more comprehensive user data. NavBoost remains central to Google's algorithm, refining search results based on click data.
NavBoost uses various user signals to refine search results:
GoodClicks and BadClicks: Assesses click quality and subsequent user behavior.
LastLongestClicks: Measures dwell time to evaluate content relevance.
UnicornClicks: Identifies rare but high-quality clicks.
These signals are crucial for enhancing user experience and ensuring the prominence of relevant content.

QualityBoost
QualityBoost evaluates the quality of search results and makes necessary adjustments to improve user satisfaction. It considers factors like content relevance, user engagement, and feedback from Google's quality raters.
RealTimeBoost
RealTimeBoost adapts search results based on current events and trends, ensuring that users receive the most up-to-date and relevant information. This twiddler reacts to breaking news, trending topics, and other real-time data to adjust search rankings dynamically.
Title Tag Significance
Title tags succinctly describe a webpage's content and are crucial for both user experience and SEO.
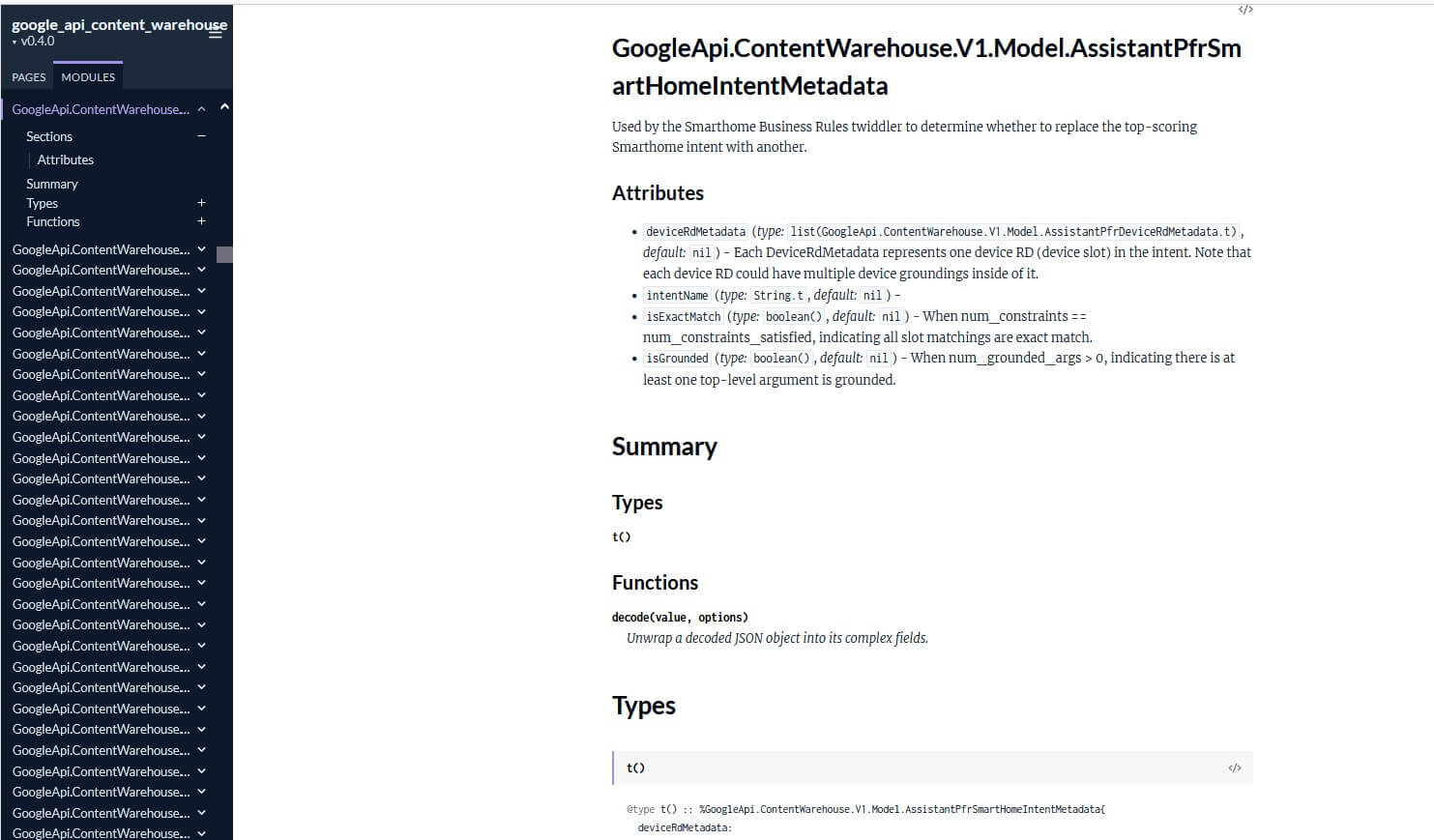
TitlematchScore
TitlematchScore measures how well a page's title aligns with user queries. A high titlematchScore indicates that the title is relevant and closely matches what users are searching for, improving the page's chances of ranking higher.
HtmlTitleFp
HtmlTitleFp ensures the authenticity and consistency of a page's title by comparing it to other metadata. This helps Google verify that the title accurately represents the page's content and is not misleading.
VideoContentSearchSpanDolphinFeatures
This feature evaluates video titles in content ranking. Given the growing importance of video content, optimizing video titles to be descriptive and relevant can significantly impact search visibility.
Keyword Utilization
Keywords categorize content and establish its relevance to specific queries.
Entity Keywords and Phrases
Entity keywords and phrases are essential for entity profiles, helping Google understand the context and relevance of content related to specific entities. Using well-researched and strategically placed keywords can enhance a page's discoverability.
Anchor Quality
Keywords in anchors enhance link relevance and quality. Google evaluates the text used in hyperlinks to determine the context and importance of the linked content, influencing how these links are weighed in the ranking algorithm.
Document NLP Analysis
Google uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to identify and analyze named entities, keywords, and key phrases within a document. This analysis helps Google understand the content's context, relevance, and overall quality.
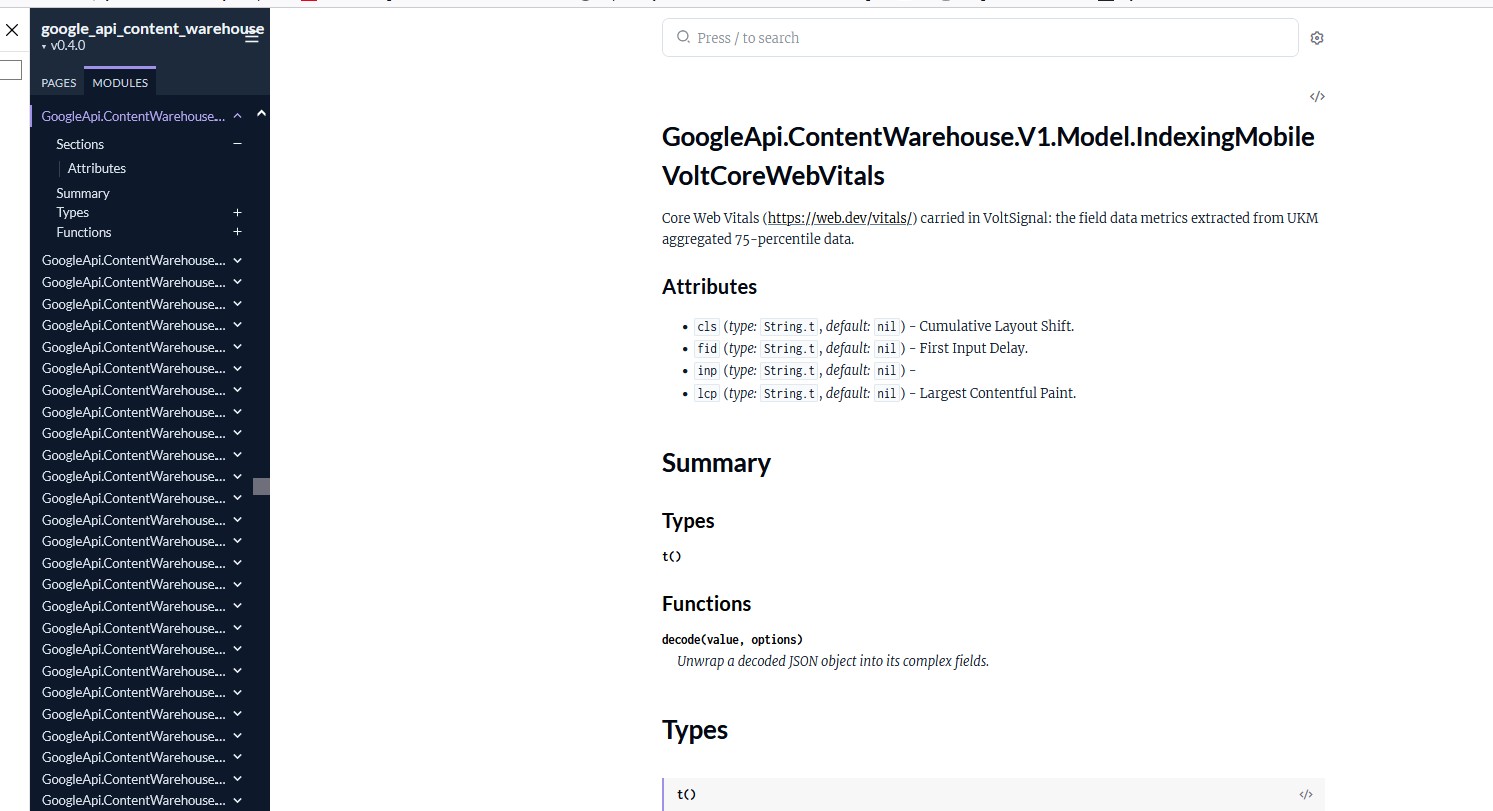
Core Web Vitals (VoltSignal)
VoltSignal evaluates Core Web Vitals, crucial metrics for assessing webpage performance and user experience.
VoltSignal Usage
VoltSignal data is stored in the Legacy Data Muppet Facility for VOLT and influences ranking adjustments. These metrics include loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability, which are critical for providing a good user experience.
Stored Components
Only Core Web Vitals (CWV) and secure signals are stored in this system. This indicates that Google places significant emphasis on these metrics when determining a page's rank.
Anchor Handling
Google tracks various anchor attributes to assess link relevance and trustworthiness.
AnchorsAnchor
AnchorsAnchor records information like original text, font size, and the appearance date of anchors. This data helps Google evaluate the quality and relevance of links.
Anchor Context
Anchor Context evaluates the surrounding content to determine the relevance and context of the anchor text. This helps Google understand how the link fits within the overall content of the page.
sourceType
sourceType determines the quality of the link source, categorizing links based on their origin. High-quality sources are more likely to positively influence a page's ranking.
Geographic and Demographic Adjustments
Google customizes search results using geographic and demographic data.
AbuseiamGeoRestrictionLocale
AbuseiamGeoRestrictionLocale restricts content access based on the user's region. This ensures that content is relevant and appropriate for users in specific geographic locations.
NavBoost Geo-Fences
NavBoost Geo-Fences uses click data by location to optimize search relevance. This helps Google deliver more accurate and contextually appropriate results to users based on their geographic location.
Age and Gender Data
Google uses age and gender data to improve content personalization and relevance. This demographic information helps tailor search results to better meet the needs and preferences of different user groups.
Author and Site Authority
Google evaluates authors and site authority to gauge trustworthiness and relevance.
Author Information
AppsPeopleOzExternalMergedpeopleapiAuthor stores details about authors and their publications. This data helps Google assess the credibility and expertise of content creators.
SiteAuthority
SiteAuthority assesses a website's overall quality based on factors like link quality, user engagement, and content relevance. A higher site authority indicates a more trustworthy and authoritative site, which can positively impact search rankings.
AbuseIAm Modules
These modules manage content classification and restrictions related to abuse.
AbuseiamAbuseType
AbuseiamAbuseType classifies various types of abuse, such as pornography and other inappropriate content. This helps Google filter out harmful or unsuitable content from search results.
AbuseiamAgeRestriction
AbuseiamAgeRestriction sets age limits for accessing certain content, ensuring that age-appropriate restrictions are applied where necessary.
AbuseiamGeoRestriction
AbuseiamGeoRestriction defines geographic restrictions for content access, ensuring compliance with regional laws and cultural norms.
AppsPeople Modules
These modules store user profile information, including interactions, interests, and social connections.
User Profiles
AppsPeopleOzExternalMergedpeopleapiPerson integrates data from multiple sources into a single user profile. This comprehensive profile helps Google deliver personalized search results based on user preferences and behavior.
User Interests
AppsPeopleOzExternalMergedpeopleapiInterest tracks user interests to provide more relevant search results. This module helps Google understand user preferences and tailor search results accordingly.
User Interactions
AppsPeopleOzExternalMergedpeopleapiActivityStreamqualityDistillerEngagements analyzes user interactions to improve search result quality. This data helps Google refine its algorithms based on real user behavior and engagement.
6. Whitelists and Special Restrictions
Google uses whitelists and specific restrictions to prioritize trusted websites in search results.
Content Display Conditions
AbuseiamVerdictRestriction applies specific conditions for content display, ensuring that only trusted and relevant content is shown under certain circumstances.
Authority Use
Modules like isCovidLocalAuthority and isElectionAuthority demonstrate the use of whitelists during significant events such as the Covid-19 pandemic and elections. These whitelists ensure that accurate and authoritative information is prioritized in search results.
7. Additional Insights from the Leak
Privacy and Browser Data Usage
Google's use of Chrome browser data for ranking evaluation is controversial. The ChromeInTotal module shows that user behavior data is analyzed for page quality evaluation, highlighting Google's reliance on comprehensive user data to refine search results.
Functionality of NavBoost
NavBoost uses click data to refine search results, considering click quantity and duration. It highlights Google's meticulous analysis of user interactions to determine content relevance and quality.
Incorporation of Quality Rater Feedback
The documents reveal that Google incorporates feedback from Quality Raters into its algorithms, influencing rankings. It has long been known that Google uses a rating system called EWOK. The recent leak provides concrete evidence that signals generated by Quality Raters are actually used in search algorithms and not just for testing purposes. The documents show that these signals are integrated into various modules and play an active role in fine-tuning and improving search results. While the exact usage and impact of these signals are not always clear, it is evident that they have more than just an experimental character.
The documents reveal that Google incorporates feedback from Quality Raters into its algorithms, influencing rankings. Specifically:
Signal Integration into Modules: Feedback from Quality Raters is not merely for testing; it is actively incorporated into various algorithmic modules. The documents provide specific annotations indicating that these signals influence the search rankings directly, rather than being confined to experimental setups
Data Collection and Utilization: The documents detail how Quality Raters' evaluations and data are collected and utilized within Google's search systems. These processes are meticulously recorded in the logs of various modules, underscoring their significance in the ranking algorithms
Active Role of Signals: Although the exact impact of these rater-based signals can sometimes be ambiguous, several sections in the documents highlight their role in refining and enhancing search results. This demonstrates that the data from Quality Raters actively contributes to Google's search algorithms, affirming their importance beyond mere experimentation
In summary, the evidence confirms that signals from Quality Raters play a crucial role in Google's search systems, significantly affecting the search rankings and proving to be integral to the algorithmic processes.
Geo-Fencing of Click Data
Geo-fencing segments click data by geographic location, ensuring search queries and clicks are evaluated differently based on region. This approach helps Google deliver more localized and relevant search results.
8. Weighting of Ranking Factors
The documents do not provide explicit details on the weighting of ranking factors but reference various signals at different points. Understanding these signals can help SEO professionals prioritize their optimization efforts.
Relevant Points Include:
PageRank Weighting: PageRank weights stored in link maps for the algorithm.
Core Web Vitals (VoltSignal): Summarizes loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
Mobile Friendliness: Stored separately as a crucial ranking signal.
Secure Signals: HTTPS and other secure signals influence ranking.
Link Data: Information on outgoing links and their quality.
Entity and Mention Scores: Used to evaluate content relevance.
User Behavior: Click-through rates and user interactions serve as signals.
Content Quality: Quality and originality impact ranking.
Navigation Attributes: Describe user interaction and navigation signals like click-through rates.
9. SEO Implications and Best Practices
Producing High-Quality Content
Google prioritizes original, high-quality content. Pages should:
Emphasize Originality: Unique, informative content is preferred.
Enhance User-Friendliness: Well-structured and readable content is crucial.
Strategic Keyword Placement: Use keywords naturally and contextually.
Enhancing User Engagement
User behavior significantly influences site evaluation.
Increase Dwell Time: Longer page stays indicate quality content.
Optimize Click Behavior: Positive interactions like longer clicks and low bounce rates are beneficial.
Effective Link Building Strategies
Links are central to ranking.
Ensure Diversity and Relevance: A diverse, relevant link structure is crucial.
Prioritize Link Quality: High-quality links from trusted sources have a greater impact.
Leveraging Core Web Vitals
To improve rankings, webmasters should focus on optimizing Core Web Vitals, ensuring fast loading times, interactivity, and visual stability. Regularly monitoring these metrics using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can help maintain high performance.
Mobile Friendliness
Given the increasing use of mobile devices for internet access, ensuring that websites are mobile-friendly is essential. This includes using responsive design, optimizing images for mobile, and ensuring quick load times on mobile networks.
10. FAQs on the Google Algorithm Leak
How can one access the leaked documents? Click here for the documents.
Does Google still use the PageRank Algorithm? Yes, the documents confirm that PageRank remains a foundational aspect of Google's ranking system, albeit in a more sophisticated form.
How does Google use 'siteAuthority' despite denying 'Domain Authority'? SiteAuthority evaluates a website's overall quality based on various factors, similar to the concept of Domain Authority, but Google uses its metrics and criteria.
What role does 'NavBoost' play in Google's ranking systems? NavBoost refines search results based on user click data, enhancing the relevance and quality of search results.
How does Google use click data to influence search rankings? Click data is analyzed to assess user engagement and satisfaction, influencing rankings through metrics like GoodClicks, BadClicks, LastLongestClicks, and UnicornClicks.
What are 'Twiddlers' and how do they affect Google's ranking algorithms? Twiddlers adjust a document's ranking score or placement before it's displayed to users, promoting diversity and relevance in search results.
What are the AbuseIAm modules and their functions? AbuseIAm modules manage content classification and restrictions related to abuse, such as pornography, age limits, and geographic restrictions.
How does geographic location affect search results? Geo-fencing segments click data by region, ensuring search results are localized and relevant to users' geographic locations.
How is link quality evaluated? Google evaluates backlinks based on their anchor text and surrounding context, with links from high-quality and authoritative pages being more valuable. Freshness and the overall quality of the linking page are crucial, while spammy and redundant links are penalized. Both direct and indirect links are considered, emphasizing the importance of diverse and relevant link sources.
What role do user interactions play in Google's evaluation process? User interactions, such as click-through rates and dwell time, are critical signals that influence content relevance and ranking.
11. Conclusion
The extensive leak of Google's ranking algorithms has uncovered numerous previously unknown aspects of Google Search's operation. For SEOs and digital marketers, this insight provides valuable information to refine strategies and achieve greater success. The detailed revelations about various modules and their functions illustrate the complexity and thoroughness of Google's evaluation process. It remains to be seen how Google will respond to this leak and its long-term impact on the SEO community.


